Overview
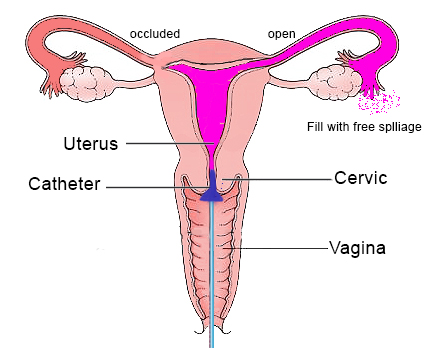
A hysterosalpingogram or HSG is an important test of female fertility potential. The HSG is a test in which a soft plastic catheter is inserted through the cervix up into the uterus and used to inject a colorless iodine-based dye into the uterus, while under a video-like x-ray system called fluoroscopy. The test is scheduled after the end of the menstrual cycle and before the ovulation to avoid exposing a pregnancy to radiation or dye.
Uses of the HSG
The procedure can be used to investigate repeated miscarriages that result from congenital or acquired abnormalities of the uterus and to determine the presence and severity of these abnormalities, including: